SIMULATION BASED TRAINING
What is Simulation Based Training?
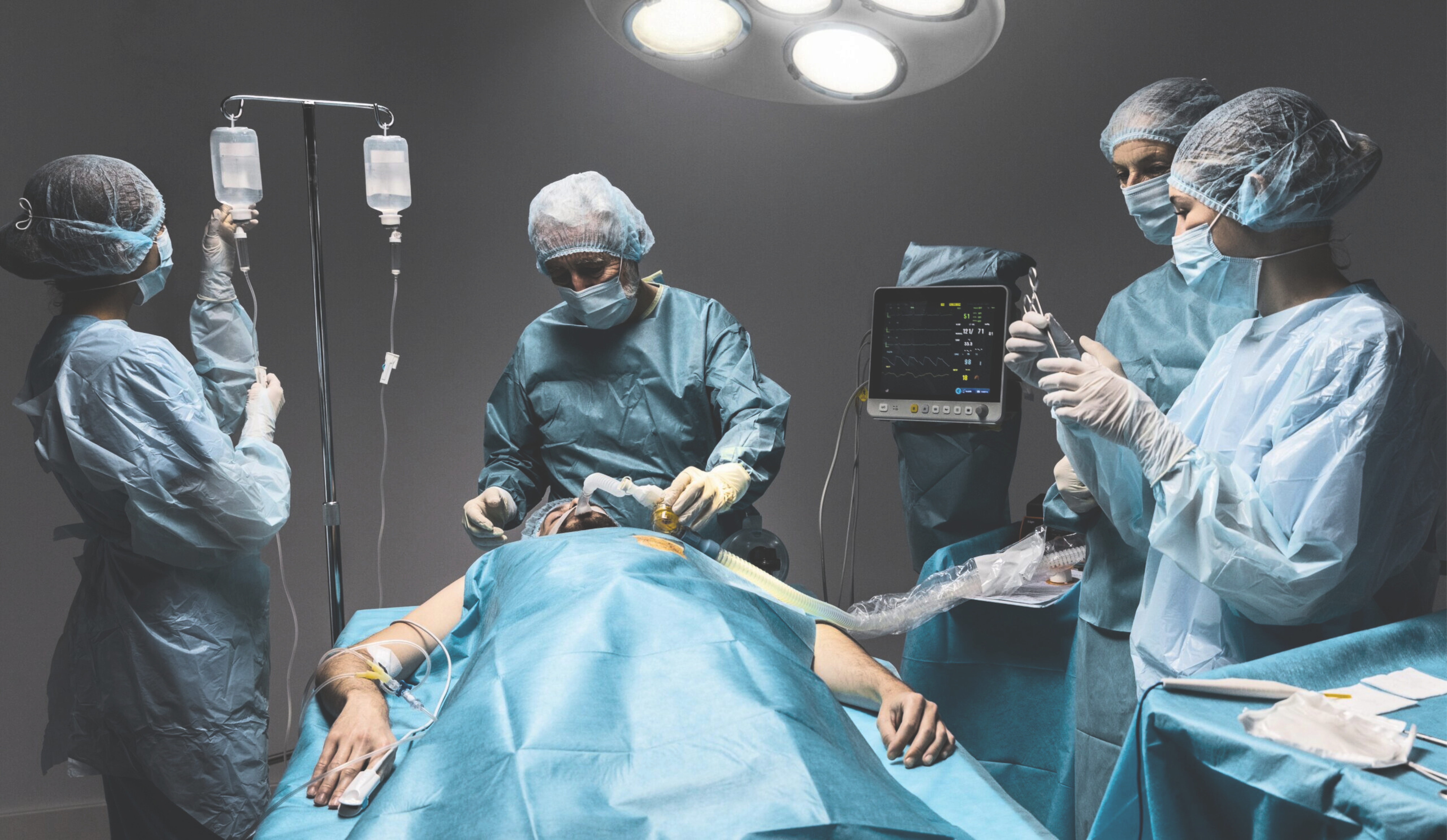
“Simulation education is a bridge between claasroom learning and real-life clinical experience. We trained the doctors and nurses on computerized mannequins that perform dozens of human functions realistically in a healthcare settings such as critical care unit that is indistinguishable from the real thing.”
“Simulation based trainings gives delegate full exposure to the real life scanerios.”
Incorporate realistic simulation scenarios that mimic various anesthesia crises. Simulations allow participants to practice and apply their skills in a controlled environment, promoting hands-on experience and better retention of knowledge.
Multidisciplinary Approach. Anesthesia crises often require collaboration among various healthcare professionals. Include training scenarios that involve teamwork and communication with other members of the healthcare team, such as surgeons, nurses, and respiratory therapists.
Scenario Variety:
Address a diverse range of crisis scenarios that an anesthesia team may encounter. This could include airway management issues, hemodynamic instability, allergic reactions, equipment failure, and other critical situations.
Real-Time Feedback:
Provide immediate feedback to participants during and after simulations. This helps individuals understand their performance, learn from the experience, and make improvements. Feedback can come from instructors, peers, or through technology.
Evidence-Based Practices:
Base your training on current evidence-based guidelines and best practices in anesthesia crisis management. Keeping the training content up-to-date ensures that participants are learning the most effective and relevant approaches.
Incorporate Technology:
Utilize advanced technologies such as virtual reality, computer-based simulations, and interactive educational tools to enhance the training experience. These technologies can provide a more immersive and engaging learning environment.
Case-Based Learning:
Integrate case studies into the training curriculum. Real-life examples help participants apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, improving their ability to think critically during crises.
Communication Skills Training:
Emphasize effective communication skills, both within the anesthesia team and when interacting with other healthcare professionals. Clear and concise communication is crucial during crisis situations.
Patient-Centered Approach:
Highlight the importance of maintaining a patient-centered approach even during crises. Participants should be trained to manage crises while prioritizing patient safety, comfort, and well-being.
Continuous Improvement:
Foster a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage participants to engage in debriefing sessions after simulations, discuss what went well, identify areas for improvement, and collectively brainstorm strategies for better crisis management.
Interprofessional Training:
Consider interprofessional training sessions where anesthesia teams work collaboratively with other healthcare providers. This helps build a cohesive and well-coordinated approach to crisis management.
Regular Updates and Refreshers:
Offer regular updates and refresher courses to keep anesthesia providers current with the latest advancements in anesthesia practice and crisis management techniques.
By incorporating these elements into your training program, you can ensure that anesthesia providers are well-prepared to handle crises effectively, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes and safety.
